- en
- fr
Table of Contents
How to build a BSDRP router lab
Instructions for launching full-mesh topology with Qemu/VirtualBox/bhyve scripts or with GNS3
BSDRP Virtual lab scripts
BSDRP provide some scripts for setting-up labs with Qemu/KVM, Virtualbox or bhyve.
bhyve
If you want to use bhyve, here is the BSDRP bhyve lab shell script.
fetch --no-verify-peer -o BSDRP-lab-bhyve.sh "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ocochard/BSDRP/master/tools/BSDRP-lab-bhyve.sh" chmod +x BSDRP-lab-bhyve.sh
Usage of this script is:
Usage: ./BSDRP-lab-bhyve.sh [-dhp] -i FreeBSD-disk-image.img [-n vm-number] [-l LAN-number] -c Number of core per VM (default 1) -d Delete All VMs, including the template -h Display this help -i filename FreeBSD file image -l X Number of LAN common to all VM (default 0) -m X RAM size (default 256M) -n X Number of VM full meshed (default 1) -p Patch FreeBSD disk-image for serial output -w dirname Working directory (default /tmp/BSDRP) This script needs to be executed with superuser privileges
Qemu/KVM
Patched release of Qemu can be found:
- FreeBSD: Included (GNS3 option)
- Windows: GNS3's qemu 0.13.0
Under FreeBSD or Linux
If you want to use Qemu or KVM, here is the BSDRP qemu/kvm lab shell script.
fetch -o BSDRP-lab-qemu.sh "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ocochard/BSDRP/master/tools/BSDRP-lab-qemu.sh" chmod +x BSDRP-lab-qemu.sh
Linux users have to replace fetch by wget.
This script was tested with qemu 0.11.1 on FreeBSD) and with KVM on a Debian GNU/Linux.
Usage of this script is:
Usage: ./BSDRP-lab-qemu.sh [-s] -i BSDRP-full.img [-n router-number] [-l LAN-number] -i filename BSDRP file image path -n X Lab mode: start X routers (between 2 and 9) full meshed -l Y Number of LAN between 0 and 9 (in lab mode only) -s Enable a shared LAN with Qemu host -h Display this help Note: In lab mode, the qemu process are started in snapshot mode, this mean that all modifications to disks are lose after quitting the lab Script need to be started with root if you want a shared LAN with the Qemu host
Under Windows
There is a VBScript for windows on irom's Blog: BSDRP – QEMU VBScript
Virtualbox
Under Windows
If you are under MS Windows, here is a BSDRP Virtualbox lab PowerShell script (need PowerShell and .Net).
For starting this PS script you need to:
- Permit Unrestricted PowerShell script execution (into a powershell started with administrative right, enter: Set-ExecutionPolicy unrestricted)
- Unblock the BSDRP-lab script, by righ-clicking on it and selecting properties then click on unblock
Pre-requise:
- VirtualBox 4.2
- A RDP client for lab based on BSDRP vga release (included in Windows: mstsc)
Steps:
- Download a BSDRP image and decompress the xz archive (using 7-zip as example) for obtaining the .img
- Right-click on the BSDRP-lab-vbox.ps1 and select “execute with PowerShell”
After use, if you want to use a new BSDRP image for the lab, delete all Virtualbox BSDRP_lab_* VM. The script will generate a BSDRP-Putty-sessions.reg file on your desktop: Import this file to your registration database for auto-configuring Putty&Kitty sessions.
Under FreeBSD or Linux
If you want to use Virtualbox, here is the BSDRP Virtualbox shell lab script.
fetch "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ocochard/BSDRP/master/tools/BSDRP-lab-vbox.sh" chmod +x BSDRP-lab-vbox.sh
Linux users have to replace fetch by wget.
Pre-requise:
- FreeBSD
- Linux
- Virtualbox (non OSE) 4.2
- socat installed for using the BSDRP serial release
- A VNC/RDP client for connecting the BSDRP vga release
Usage: /usr/local/BSDRP/tools/BSDRP-lab-vbox.sh [-hdsv] [-a i386|amd64] [-i BSDRP_image_file.img] [-n router-number] [-l LAN-number] [-o serial|vga]
-a ARCH Force architecture: i386 or amd
This disable automatic arch/console detection from the filename
You should use -o with -a
-c Enable internal NIC shared with host for each routers (default: Disable)
-d Delete all BSDRP VM and disks
-i filename BSDRP image file name (to be used the first time only)
-h Display this help
-l Y Number of LAN between 0 and 9 (default: 0)
-m RAM (in MB) for each VM (default: 192)
-n X Number of router (between 1 and 9) full meshed (default: 1)
-o CONS Force console: vga (default if -a) or serial
-s Stop all VM
-v Enable virtio drivers
Example of use
Using qemu:
./BSDRP-lab-qemu.sh -n 4 -l 2 -i BSDRP.i386.img
or with VirtualBox script:
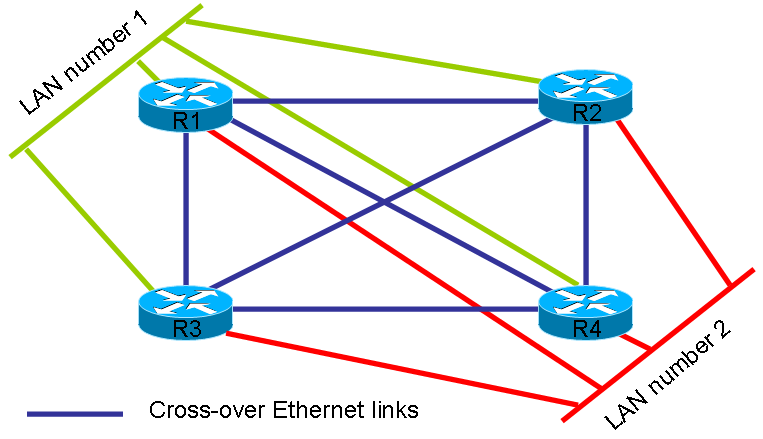
./BSDRP-lab-vbox.sh -n 4 -l 2 -i BSDRP_0.36_full_amd64_serial.img BSD Router Project (http://bsdrp.net) - VirtualBox lab script Image file given... rebuilding BSDRP router template and deleting all routers x86-64 image serial image Creating lab with 4 router(s): - 2 LAN between all routers - Full mesh Ethernet links between each routers Router1 have the following NIC: em0 connected to Router2. em1 connected to Router3. em2 connected to Router4. em3 connected to LAN number 1. em4 connected to LAN number 2. Router2 have the following NIC: em0 connected to Router1. em1 connected to Router3. em2 connected to Router4. em3 connected to LAN number 1. em4 connected to LAN number 2. Router3 have the following NIC: em0 connected to Router1. em1 connected to Router2. em2 connected to Router4. em3 connected to LAN number 1. em4 connected to LAN number 2. Router4 have the following NIC: em0 connected to Router1. em1 connected to Router2. em2 connected to Router3. em3 connected to LAN number 1. em4 connected to LAN number 2. Connect to router 1: socat unix-connect:/tmp/BSDRP_lab_R1.serial STDIO,raw,echo=0 Connect to router 2: socat unix-connect:/tmp/BSDRP_lab_R2.serial STDIO,raw,echo=0 Connect to router 3: socat unix-connect:/tmp/BSDRP_lab_R3.serial STDIO,raw,echo=0 Connect to router 4: socat unix-connect:/tmp/BSDRP_lab_R4.serial STDIO,raw,echo=0
This will start 4 routers full-meshed (ethernet cross-over cable) and each routers connected to 2 LAN:
GNS3
If you would testing BSDRP integration with Cisco/Juniper devices,GNS3 is a great tools.
VirtualBox
Latest release of GNS3 support the use of virtualbox guest: The guest speed with virtualbox is a lot's better than with Qemu.
Preparing BSDRP image disk for VirtualBox
Download a full i386/amd65 BSDRP serial image and un-xz it (using 7-zip)… you should obtain a .img file (not a .xz file!).
Using a serial image will permit to prevent keyboard mapping problem: We will connect to the console with a virtual serial port and Putty.
We need to convert the RAW BSDRP .img file to a .vdi VirtualBox hard drive image using the command-line only "VBoxManage convertfromraw".
Under MS Windows this is done by opening a cmd.exe window and entering:
C:\Users\Olivier>cd %VBOX_INSTALL_PATH% C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox>VBoxManage convertfromraw D:\BSDRP_1.1_full_amd64_serial.img D:\BSDRP_1.1_full_amd64_serial.vdi Converting from raw image file=D:\BSDRP_1.1_full_amd64_serial.img to file=D:\BSDRP_1.1_full_amd64_serial.vdi... Creating dynamic image with size 256000000 bytes (245MB)... C:\Program Files\Oracle\VirtualBox>
Create a BSDRP VM under VirtualBox
Now start VirtualBox and create a new VM:
- Name: What you want
- OS: BSD
- Version: “FreeBSD” or “FreeBSD (64 bits)” regarding your BSDRP image
- RAM: 128Mo minimum
- Hard Drive: Use existing, and select your freshly converted .vdi BSDRP image file
Then, only if you are using the “serial” BSDRP image, edit your VM:
- Serial Port: Port 1
- Enable
- Mode: Host pipe
- Check the case: Create pipe
- port path: \\.\pipe\YOUR_VM_NAME
You can test your settings by starting your VM and launch PuTTY with theses parameters:
- Connection type: serial
- serial port: \\.\pipe\YOUR_VM_NAME
- Speed: 115200
You should see the bootloader and dmesg, now shutdown your VM.
Declaring a VirtualBox Guest
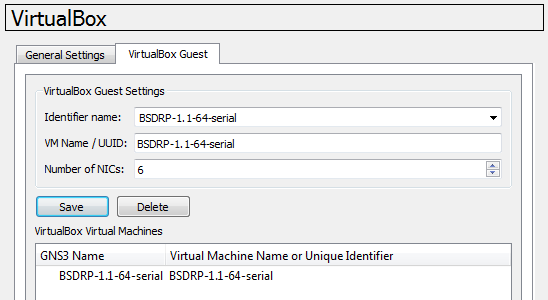
Under GNS3, go to “Edit” ⇒ “Preferences…” ⇒ “VirtualBox” ⇒ “VirtualBox Guest”
And simply select the BSDRP Vbox VM.
Qemu
Use Qemu only if you can use the KVM acceleration feature (GNS3 under GNU/Linux only), if not: Use the virtualbox guest.
Preparing BSDRP i386 VGA image for GNS3's Qemu
Download a full i386 BSDRP VGA and un-xz it (using 7-zip)… you should obtain a .img file (not a .xz file!).
Don't use a 64bit image: GNS3's Qemu is configured for running 32bits guest only.
Declaring a Qemu Guest
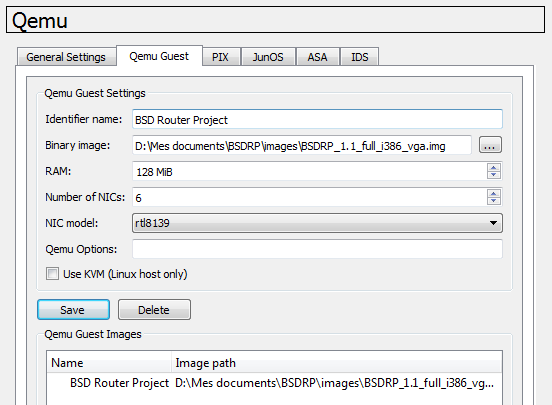
Under GNS3, go to “Edit” ⇒ “Preferences…” ⇒ “Qemu” ⇒ “Qemu Guest”
And simply give the path to the BSDRP vga image.
Troubleshooting
If when you try starting your BSDRP qemu host you have this message:
“CPU doesn't support long mode”
This mean your are trying to start a 64bits OS on your 32bits emulated guest.