- en
- fr
Table of Contents
IPSec performance lab of a PC Engines APU
IPSec performance lab of a PC Engines APU
Hardware detail
This lab will test a PC Engines APU 1 (dmesg):
- Dual core AMD G-T40E Processor (1 GHz)
- 3 Realtek RTL8111E Gigabit Ethernet ports
- 2Gb of RAM
Lab set-up
For more information about full setup of this lab: Setting up a forwarding performance benchmark lab (switch configuration, etc.).
A current version of BSDRP-1.9997 based on FreeBSD 11-current r262847 (10-stable didn't boot on this board) is used on the packet generator, receiver and the DUT.
Diagram
+---------------------+ +-------------------------------------+ +----------------------------------------+
| R1 | | PC Engines APU | | R3 |
| Packet generator | | Device under Test | | IPSec endpoint |
| and receiver | | | | (AES-NI) |
| | | | | |
|igb2: 198.18.0.201/24|=>=| re1: 198.18.0.207/24 | | |
| 2001:2::201/64| | 2001:2::207/64 | | |
| 00:1b:21:d4:3f:2a| | 00:0d:b9:3c:dd:3d | | |
| | | | | |
| | | re2: 198.18.1.207/24 |==>=| igb2: 198.18.1.203/24 |
| | | 2001:2:0:1::207/64 | | 2001:2:0:1::203/64 |
| | | 00:0d:b9:3c:dd:3e | | 00:1b:21:c4:95:7a |
| | | | | |
| | | static routes | | static routes |
| | | 198.19.0.0/16 => 198.18.1.203 | | 198.19.0.0/16 => 198.19.0.201 |
| | | 198.18.0.0/16 => 198.18.0.201 | | 198.18.0.0/16 => 198.18.1.207 |
| | | 2001:2::/49 => 2001:2::201 | | 2001:2::/49 => 2001:2:0:1::207 |
| | |2001:2:0:8000::/49 => 2001:2:0:1::203| | 2001:2:0:8000::/49=>2001:2:0:8000::201 |
| | | | | |
|igb3: 198.19.0.201/24| | | | igb3: 198.19.0.203/24 |
|2001:2:0:8000::201/64| | | | 2001:2:0:8000::203/64 |
| 00:1b:21:d4:3f:2b | | | | 00:1b:21:c4:95:7b |
+---------------------+ +-------------------------------------+ +----------------------------------------+
|| ||
==================================<============================================
Devices configuration
R1 (Packet generator/receiver)
ifconfig igb2 up ifconfig igb3 up
APU (DUT)
Disable fastforwarding (not compliant with IPSec), configure IP address, routes and static IPSec.
/etc/rc.conf
# Hostname hostname="APU" # Disable INTERRUPT and ETHERNET from entropy sources harvest_mask="351" # IPv4 router gateway_enable="YES" ifconfig_re1="inet 198.18.0.207/24" ifconfig_re2="inet 198.18.1.207" static_routes="generator receiver" route_generator="-net 198.18.0.0/16 198.18.0.201" route_receiver="-net 198.19.0.0/16 198.18.1.203" static_arp_pairs="receiver generator" static_arp_generator="198.18.0.201 00:1b:21:d4:3f:2a" static_arp_receiver="198.18.1.203 00:1b:21:c4:95:7a" # IPv6 router ipv6_gateway_enable="YES" ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES" ipv6_static_routes="generator receiver" ipv6_route_generator="2001:2:: -prefixlen 49 2001:2::201" ipv6_route_receiver="2001:2:0:8000:: -prefixlen 49 2001:2:0:1::203" ifconfig_re1_ipv6="inet6 2001:2::207 prefixlen 64" ifconfig_re2_ipv6="inet6 2001:2:0:1::207 prefixlen 64" static_ndp_pairs="receiver generator" static_ndp_generator="2001:2::201 00:1b:21:d4:3f:2a" static_ndp_receiver="2001:2:0:1::203 00:1b:21:c4:95:7b" # Enabling IPSec ipsec_enable="YES"
/etc/ipsec.conf:
flush; spdflush; spdadd 198.18.0.0/16 198.19.0.0/16 any -P out ipsec esp/tunnel/198.18.1.207-198.18.1.203/require; spdadd 198.19.0.0/16 198.18.0.0/16 any -P in ipsec esp/tunnel/198.18.1.203-198.18.1.207/require; add 198.18.1.203 198.18.1.207 esp 0x1000 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456"; add 198.18.1.207 198.18.1.203 esp 0x1001 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456"; spdadd 2001:2::/49 2001:2:0:8000::/49 any -P out ipsec esp/tunnel/2001:2:0:1::207-2001:2:0:1::203/require; spdadd 2001:2:0:8000::/49 2001:2::/49 any -P in ipsec esp/tunnel/2001:2:0:1::203-2001:2:0:1::207/require; add 2001:2:0:1::203 2001:2:0:1::207 esp 0x1002 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456"; add 2001:2:0:1::207 2001:2:0:1::203 esp 0x1003 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456";
R3 (Reference device)
Disable fastforwarding (not compliant with IPSec), configure IP address, routes and static IPSec.
/etc/rc.conf:
# Hostname hostname="R3" # Disable INTERRUPT and ETHERNET from entropy sources harvest_mask="351" # IPv4 router gateway_enable="YES" ifconfig_igb2="inet 198.18.1.203/24" ifconfig_igb3="inet 198.19.0.203/24" static_routes="generator receiver" route_generator="-net 198.18.0.0/16 198.18.1.207" route_receiver="-net 198.19.0.0/16 198.19.0.201" static_arp_pairs="receiver generator" static_arp_generator="198.18.1.207 00:0d:b9:3c:dd:3e" static_arp_receiver="198.19.0.201 00:1b:21:d4:3f:2b" # IPv6 router ipv6_gateway_enable="YES" ipv6_activate_all_interfaces="YES" ifconfig_igb2_ipv6="inet6 2001:2:0:1::203 prefixlen 64" ifconfig_igb3_ipv6="inet6 2001:2:0:8000::203 prefixlen 64" ipv6_static_routes="generator receiver" ipv6_route_generator="2001:2:: -prefixlen 49 2001:2:0:1::207" ipv6_route_receiver="2001:2:0:8000:: -prefixlen 49 2001:2:0:8000::201" static_ndp_pairs="receiver generator" static_ndp_generator="2001:2:0:1::207 00:0d:b9:3c:dd:3e" static_ndp_receiver="2001:2:0:8000::201 00:1b:21:d4:3f:2b" # Enabling IPSec kld_list="aesni" ipsec_enable="YES"
/etc/ipsec.conf:
flush; spdflush; spdadd 198.18.0.0/16 198.19.0.0/16 any -P in ipsec esp/tunnel/198.18.1.207-198.18.1.203/require; spdadd 198.19.0.0/16 198.18.0.0/16 any -P out ipsec esp/tunnel/198.18.1.203-198.18.1.207/require; add 198.18.1.203 198.18.1.207 esp 0x1000 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456"; add 198.18.1.207 198.18.1.203 esp 0x1001 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456"; spdadd 2001:2::/49 2001:2:0:8000::/49 any -P in ipsec esp/tunnel/2001:2:0:1::207-2001:2:0:1::203/require; spdadd 2001:2:0:8000::/49 2001:2::/49 any -P out ipsec esp/tunnel/2001:2:0:1::203-2001:2:0:1::207/require; add 2001:2:0:1::203 2001:2:0:1::207 esp 0x1002 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456"; add 2001:2:0:1::207 2001:2:0:1::203 esp 0x1003 -E rijndael-cbc "1234567890123456";
Using IPSec bench "Equilibrium throughput" method
Once done, we start using a fast method for measuring the “IPsec equilibrium throughput” of the DUT.
Notice that the reference device (IBM x3550-M3) used in front of the PC Engines APU1 has a equilibrium throughput of 843Mb/s. Then if the value measured during this bench is close to 843Mb/s we had to found a more powerful reference device.
From the packet generator/receiver a simple script that use netmap-pktgen will do the job:
[root@R1]# equilibrium -l 100 -d 00:0d:b9:3c:dd:3d -t igb2 -r igb3 Benchmark tool using equilibrium throughput method - Benchmark mode: Bandwitdh (bps) for VPN gateway - UDP load = 500B, IPv4 packet size=528B, Ethernet frame size=542B - Link rate = 100 Mb/s - TOLERANCE = 0.01 Iteration 1 - offering load = 50 Mb/s - STEP = 25 Mb/s - Measured forwarding rate = 50 Mb/s Iteration 2 - offering load = 75 Mb/s - STEP = 25 Mb/s - TREND = increasing - Measured forwarding rate = 72 Mb/s Iteration 3 - offering load = 63 Mb/s - STEP = 12 Mb/s - TREND = decreasing - Measured forwarding rate = 63 Mb/s Iteration 4 - offering load = 69 Mb/s - STEP = 6 Mb/s - TREND = increasing - Measured forwarding rate = 68 Mb/s Iteration 5 - offering load = 66 Mb/s - STEP = 3 Mb/s - TREND = decreasing - Measured forwarding rate = 65 Mb/s Estimated Equilibrium Ethernet throughput= 65 Mb/s (maximum value seen: 72 Mb/s)
Here is the ministat distribution:
root@R1:~ # ministat -s -w 74 apu-ipsec
x Equilibrium throughput with rijndael-cbc
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| x |
|x x x x|
| |___________________________A__________M_______________| |
+--------------------------------------------------------------------------+
N Min Max Median Avg Stddev
x 5 61 65 64 63.4 1.5165751
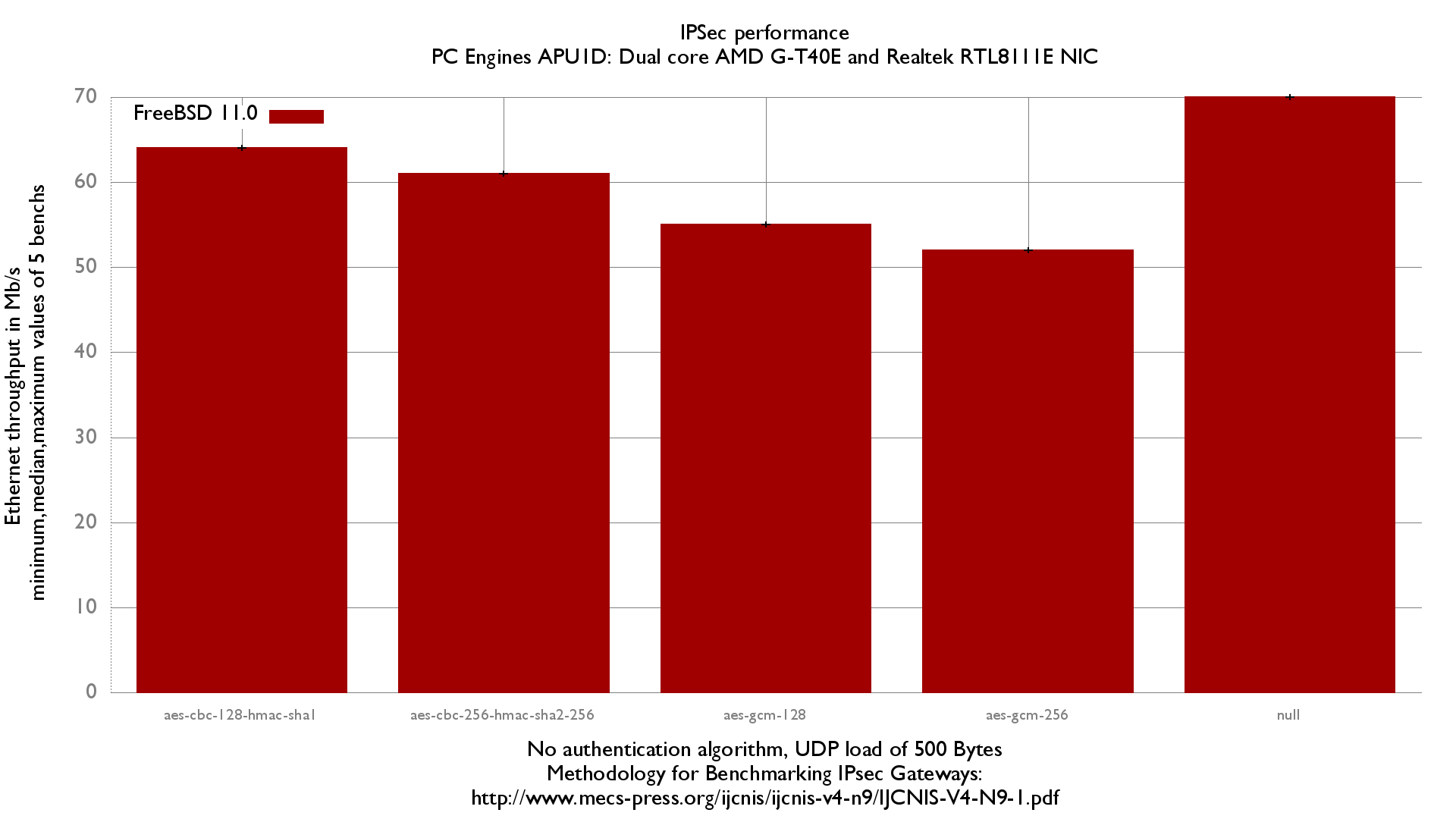
Using AES-CBC (rijndael-cbc) with a 128 bits key, we can estimate an IPSec Equilibrium throughput of 64Mb/s.
And same performance for IPv6:
[root@R1]# equilibrium -l 100 -d 00:0d:b9:3c:dd:3d -t igb2 -r igb3 -6 Benchmark tool using equilibrium throughput method - Benchmark mode: Bandwitdh (bps) for VPN gateway - UDP load = 500B, IPv6 packet size=548B, Ethernet frame size=562B - Link rate = 100 Mb/s - TOLERANCE = 0.01 Iteration 1 - offering load = 50 Mb/s - STEP = 25 Mb/s - Measured forwarding rate = 50 Mb/s Iteration 2 - offering load = 75 Mb/s - STEP = 25 Mb/s - TREND = increasing - Measured forwarding rate = 72 Mb/s Iteration 3 - offering load = 63 Mb/s - STEP = 12 Mb/s - TREND = decreasing - Measured forwarding rate = 63 Mb/s Iteration 4 - offering load = 69 Mb/s - STEP = 6 Mb/s - TREND = increasing - Measured forwarding rate = 68 Mb/s Iteration 5 - offering load = 66 Mb/s - STEP = 3 Mb/s - TREND = decreasing - Measured forwarding rate = 66 Mb/s Estimated Equilibrium Ethernet throughput= 66 Mb/s (maximum value seen: 72 Mb/s)