- en
- fr
Table of Contents
Maximum BSDRP features lab
Complex example showing some of available features This lab is used for testing BSDRP before releasing new version.
Presentation
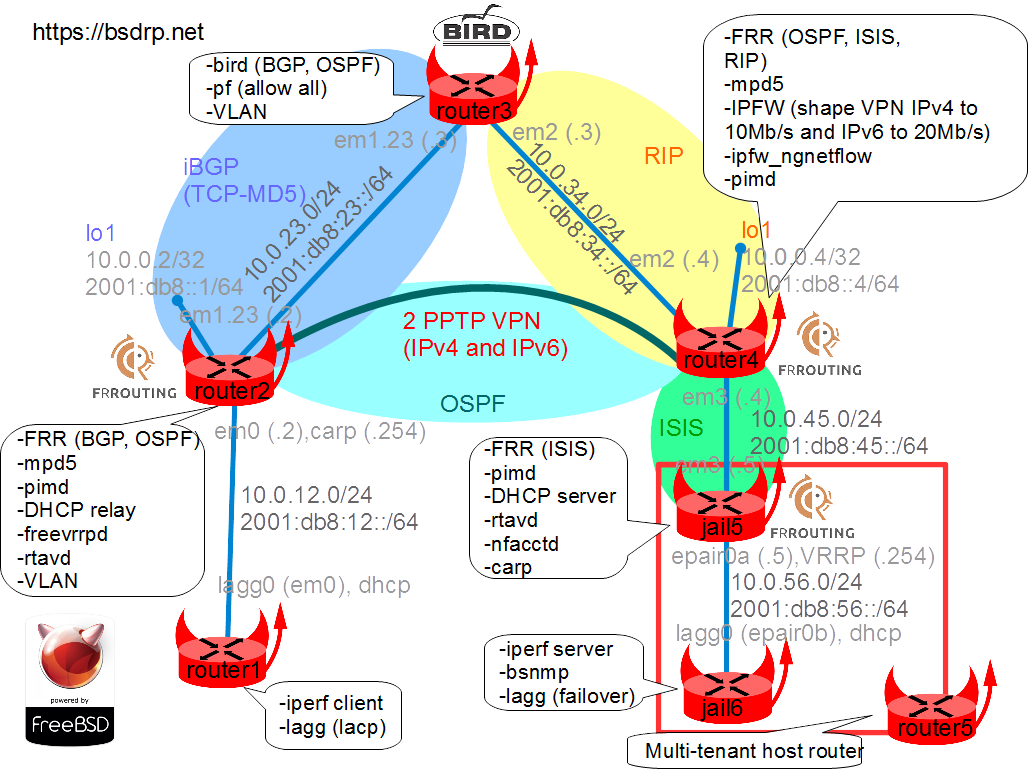
Network diagram
Setting-up the lab
Downloading BSD Router Project images
Download BSDRP serial image (prevent to have to use an X display) on Sourceforge.
Download Lab scripts
More information on these BSDRP lab scripts available on How to build a BSDRP router lab.
Start the lab with full-meshed 6 routers.
An example with bhyve under FreeBSD:
tools/BSDRP-lab-bhyve.sh -i /usr/obj/BSDRP.amd64/BSDRP-1.80-full-amd64-serial.img.xz -n 5 -e Setting-up a virtual lab with 5 VM(s): - Working directory: /tmp/BSDRP - Each VM have 1 core(s) and 256M RAM - Emulated NIC: e1000 - Switch mode: bridge + tap - 0 LAN(s) between all VM - Full mesh Ethernet links between each VM VM 1 have the following NIC: - em0 connected to VM 2 - em1 connected to VM 3 - em2 connected to VM 4 - em3 connected to VM 5 VM 2 have the following NIC: - em0 connected to VM 1 - em1 connected to VM 3 - em2 connected to VM 4 - em3 connected to VM 5 VM 3 have the following NIC: - em0 connected to VM 1 - em1 connected to VM 2 - em2 connected to VM 4 - em3 connected to VM 5 VM 4 have the following NIC: - em0 connected to VM 1 - em1 connected to VM 2 - em2 connected to VM 3 - em3 connected to VM 5 VM 5 have the following NIC: - em0 connected to VM 1 - em1 connected to VM 2 - em2 connected to VM 3 - em3 connected to VM 4 To connect VM'serial console, you can use: - VM 1 : cu -l /dev/nmdm-BSDRP.1B - VM 2 : cu -l /dev/nmdm-BSDRP.2B - VM 3 : cu -l /dev/nmdm-BSDRP.3B - VM 4 : cu -l /dev/nmdm-BSDRP.4B - VM 5 : cu -l /dev/nmdm-BSDRP.5B
Routers configuration
In this order for avoiding DHCP client timeout problems.
All these routers can be configured with labconfig tool (use it only on a lab, because it will replace your current running configuration):
labconfig full_vm[VM-NUMBER]
Router 5 (including jail5 and jail6)
(you can use script “labconfig vm5” for automatically pushing full configuration):
sysrc hostname=R5 \
ifconfig_em3=up \
cloned_interfaces=epair0 \
ifconfig_epair0a=up \
kld_list+=" if_lagg carp"
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/rc.conf
cat > /etc/devfs.rules <<EOF
[devfsrules_jailpf=4]
add include \$devfsrules_hide_all
add include \$devfsrules_unhide_basic
add include \$devfsrules_unhide_login
add path 'bpf*' unhide
EOF
hostname R5
service devfs restart
service netif restart
service kld start
if ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet; then
tenant -c -j jail5 -i vtnet3,epair0a
else
tenant -c -j jail5 -i em3,epair0a
fi
tenant -c -j jail6 -i epair0b
sysrc -f /etc/jails/jail5/rc.conf hostname=jail5 \
ifconfig_em3="inet 10.0.45.5/24" \
ifconfig_em3_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:45::5 prefixlen 64" \
ifconfig_epair0a="10.0.56.5/24" \
ifconfig_epair0a_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:56::5 prefixlen 64" \
ifconfig_epair0a_alias0="inet 10.0.56.254/32 vhid 1 pass testpass" \
ifconfig_epair0a_alias1="inet6 2001:db8:56::fe prefixlen 128 vhid 1 pass testpass" \
rtadvd_enable=YES \
rtadvd_interfaces=epair0a \
dhcpd_enable=YES \
dhcpd_flags="-q" \
dhcpd_conf="/usr/local/etc/dhcpd.conf" \
frr_enable=YES \
frr_vtysh_boot=YES \
nfacctd_enable=YES \
pimd_enable=YES
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/jails/jail5/rc.conf
mkdir -p /etc/jails/jail5/local/frr
cat > /etc/jails/jail5/local/dhcpd.conf <<EOF
option domain-name "bsdrp.net";
default-lease-time 600;
max-lease-time 7200;
ddns-update-style none;
#Declare useless network
subnet 10.0.45.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
}
#Declare R1 LAN and gateway
subnet 10.0.12.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.0.12.1 10.0.12.1;
option routers 10.0.12.254;
}
#Declare R6 subnet and gateway
subnet 10.0.56.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 {
range 10.0.56.6 10.0.56.6;
option routers 10.0.56.254;
}
EOF
cat > /etc/jails/jail5/local/frr/frr.conf <<EOF
frr version 7.0
frr defaults traditional
hostname jail5
log syslog
!
interface em3
ip router isis BSDRP
ipv6 router isis BSDRP
!
interface epair0a
ip router isis BSDRP
ipv6 router isis BSDRP
isis passive
!
interface vtnet3
ip router isis BSDRP
ipv6 router isis BSDRP
!
router isis BSDRP
is-type level-1-2
net 49.0001.1720.1600.5005.00
!
line vty
!
bfd
!
EOF
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/jails/jail5/local/frr/frr.conf
chown frr:frr /etc/jails/jail5/local/frr
cat > /etc/jails/jail5/local/nfacctd.conf<<EOF
daemonize: true
syslog: daemon
!
! interested in in and outbound traffic
aggregate: src_host,dst_host
nfacctd_ip: 10.0.45.5
nfacctd_port: 2055
aggregate[ip]: src_host, dst_host, timestamp_start, timestamp_end, src_port, dst_port, proto, src_as, dst_as, peer_src_ip
plugins: print[ip]
print_output: csv
print_refresh_time: 300
print_history: 5m
print_output_file[ip]: /tmp/file-%Y%m%d-%H%M.txt
print_history_roundoff: m
print_output_file_append: true
files_umask: 022
EOF
sysrc -f /etc/jails/jail6/rc.conf hostname=jail6 \
ifconfig_epair0b="up" \
cloned_interfaces="lagg0" \
ifconfig_lagg0="laggproto failover laggport epair0b SYNCDHCP" \
ifconfig_lagg0_ipv6="inet6 accept_rtadv" \
rtsold_enable=YES \
bsnmpd_enable=YES \
gateway_enable=NO \
ipv6_gateway_enable=NO
service jail start
Router 2
(you can use script “labconfig vm2” for automatically pushing full configuration):
sysrc hostname=R2
sysrc rtadvd_enable=YES
sysrc rtadvd_interfaces="em0"
sysrc vlans_em1="23"
sysrc ifconfig_em1="up mtu 1528"
sysrc ifconfig_em0="inet 10.0.12.2/24"
sysrc ifconfig_em0_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:12::2 prefixlen 64"
sysrc ifconfig_em1_23="inet 10.0.23.2/24"
sysrc ifconfig_em1_23_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:23::2 prefixlen 64"
sysrc cloned_interfaces="lo1"
sysrc ifconfig_lo1="inet 10.0.0.2/32"
sysrc ifconfig_lo1_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8::2 prefixlen 128"
sysrc frr_enable=YES
sysrc frr_vtysh_boot=YES
sysrc dhcprelya_enable=YES
sysrc dhcprelya_servers="10.0.45.5"
sysrc dhcprelya_ifaces=em0
sysrc mpd_enable=YES
sysrc mpd_flags="-b -s ppp"
sysrc ipsec_enable=YES
sysrc ipsec_file="/etc/ipsec.conf"
sysrc pimd_enable=YES
sysrc freevrrpd_enable=YES
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/rc.conf
cat > /usr/local/etc/freevrrpd.conf <<EOF
[VRID]
serverid = 1
interface = em0
# We want that this router is the master
priority = 101
addr = 10.0.12.254/24
password = vrid1
EOF
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /usr/local/etc/freevrrpd.conf
cat > /usr/local/etc/mpd5/if-up.sh <<EOF
#!/bin/sh
set -e
logger "\$0 called with parameters: \$@"
if [ "\$2" == "inet6" ]; then
if ifconfig \$1 \$2 2001:db8:24::2; then
logger "\$0: \$cmd successfull"
return 0
else
logger "\$0: \$cmd failed"
return 1
fi
else
return 0
fi
EOF
chmod +x /usr/local/etc/mpd5/if-up.sh
cat > /usr/local/etc/mpd5/mpd.conf <<EOF
# Configuring a server PPTP VPN with tunnels to R4
default:
load vpnipv4
load vpnipv6
vpnipv4:
# Create bundle called vpnipv4
create bundle static vpnipv4
# IP of client and server, on another subnet for avoiding problems
set ipcp ranges 10.4.24.2/32 10.4.24.4/32
# Remote LAN subnet: Learned by routing protocol
#set iface route 10.0.45.0/24
# Enable Microsoft Point-to-Point encryption (MPPE)
set bundle enable compression
set ccp yes mppc
set mppc yes e40
set mppc yes e128
set bundle enable crypt-reqd
set mppc yes stateless
# Create a static pptp link called lvpnipv4
create link static lvpnipv4 pptp
# Attach this link to vpnipv4
set link action bundle vpnipv4
# Set somes link settings
set link no pap
set link yes chap
set auth authname "VpnLogin4"
# Reduce the size of the outgoing packet for avoiding fragmentation
set link mtu 1460
set link keep-alive 10 75
# max-redial:
# Server side, need to be "-1"
# Client side, need to be positive (0 for allways)
set link max-redial -1
# Local WAN IP addresse
set pptp self 10.0.0.2
# Remote WAN IP addresse
set pptp peer 10.0.0.4
# Allow incoming call
set link enable incoming
vpnipv6:
# Create bundle called vpnipv6
create bundle static vpnipv6
# Don't know how to disable IPv4 ipcp
set ipcp ranges 10.6.24.2/32 10.6.24.4/32
# Enable IPv6
set bundle enable ipv6cp
# Remote LAN subnet: Learned by routing protocol
#set iface route 2001:db8:45::/64
# Need to statically set inet6 address
set iface up-script /usr/local/etc/mpd5/if-up.sh
# Enable Microsoft Point-to-Point encryption (MPPE)
set bundle enable compression
set ccp yes mppc
set mppc yes e40
set mppc yes e128
set bundle enable crypt-reqd
set mppc yes stateless
# Create a static pptp link called lvpnipv4
create link static lvpnipv6 pptp
# Attach this link to vpnipv6
set link action bundle vpnipv6
# Set somes link settings
set link no pap
set link yes chap
set auth authname "VpnLogin6"
# Reduce the size of the outgoing packet for avoiding fragmentation
set link mtu 1460
set link keep-alive 10 75
# max-redial:
# Server side, need to be "-1"
# Client side, need to be positive (0 for allways)
set link max-redial -1
# Local WAN IP addresse
set pptp self 2001:db8::2
# Remote WAN IP addresse
set pptp peer 2001:db8::4
# Allow incoming call
set link enable incoming
EOF
cat > /usr/local/etc/mpd5/mpd.secret <<EOF
VpnLogin4 VpnPassword4
VpnLogin6 VpnPassword6
EOF
cat > /etc/ipsec.conf <<EOF
flush ;
add 10.0.23.2 10.0.23.3 tcp 0x1000 -A tcp-md5 "abigpassword" ;
add 10.0.23.3 10.0.23.2 tcp 0x1001 -A tcp-md5 "abigpassword" ;
add -6 2001:db8:23::2 2001:db8:23::3 tcp 0x1002 -A tcp-md5 "abigpassword" ;
add -6 2001:db8:23::3 2001:db8:23::2 tcp 0x1003 -A tcp-md5 "abigpassword" ;
EOF
cat > /usr/local/etc/frr/frr.conf <<EOF
frr version 7.0
frr defaults traditional
hostname R2
log syslog
!
interface ng0
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 superpass
ip ospf network point-to-point
ipv6 ospf6 passive
!
interface ng1
ipv6 ospf6 network point-to-point
!
router-id 0.0.0.2
!
router bgp 100
neighbor 10.0.23.3 remote-as 100
neighbor 10.0.23.3 password abigpassword
neighbor 2001:db8:23::3 remote-as 100
neighbor 2001:db8:23::3 password abigpassword
!
address-family ipv4 unicast
network 10.0.0.2/32
neighbor 10.0.23.3 soft-reconfiguration inbound
no neighbor 2001:db8:23::3 activate
exit-address-family
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
network 2001:db8::2/128
neighbor 2001:db8:23::3 activate
neighbor 2001:db8:23::3 soft-reconfiguration inbound
exit-address-family
!
router ospf
ospf router-id 0.0.0.2
network 10.0.12.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
network 10.4.24.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
area 0.0.0.0 authentication message-digest
!
router ospf6
interface ng1 area 0.0.0.0
interface em0 area 0.0.0.0
interface vtnet0 area 0.0.0.0
!
line vty
!
bfd
!
EOF
config save
hostname R2
service netif restart
service ipsec start
service rtadvd start
service freevrrpd start
service frr start
service dhcprelya start
service mpd5 start
service pimd start
Router 3
(you can use script “labconfig vm3” for automatically pushing full configuration):
sysrc hostname=R3
sysrc vlans_em1="23"
sysrc ifconfig_em1="up mtu 1528"
sysrc ifconfig_em1_23="inet 10.0.23.3/24"
sysrc ifconfig_em1_23_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:23::3 prefixlen 64"
sysrc ifconfig_em2="inet 10.0.34.3/24 mtu 1528"
sysrc ifconfig_em2_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:34::3 prefixlen 64"
sysrc bird_enable=YES
sysrc pf_enable=YES
sysrc pf_rules="/etc/pf.conf"
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/rc.conf
cat > /etc/pf.conf <<EOF
#Variables definitions
#TO_R2_if = "{" vtnet1.23 em1.23 "}"
#TO_R4_if = "{" vtnet2 em2 "}"
#R2 = "10.0.0.2/32"
#R4 = "10.0.0.4/32"
## ALTQ rules
# Queue outgoing from \$TO_R4_if (R2 => R4)
# Rate-limit inet 4 VPN traffic to 10Mb
#altq on \$TO_R4_if hfsc bandwidth 100Mb queue { VPN4_TO_R4, OTHER_TO_R4 }
#queue VPN4_TO_R4 bandwidth 10Mb hfsc(upperlimit 10Mb)
#queue OTHER_TO_R4 bandwidth 90Mb hfsc(default)
# Queue for outgoing traffic from \$TO_R2_if (R4 => R2)
#altq on \$TO_R2_if hfsc bandwidth 100Mb queue { VPN4_TO_R2, OTHER_TO_R2 }
#queue VPN4_TO_R2 bandwidth 10Mb hfsc(upperlimit 10Mb)
#queue OTHER_TO_R2 bandwidth 90Mb hfsc(default)
## PF rules
# R2 => R4
# Shapping works on outgoing traffic only, but need to 'mark' traffic
# entering the interface for putting returning traffic in the good queue
#pass in quick on \$TO_R2_if proto gre from \$R2 to \$R4 queue VPN4_TO_R2
# Apply ALTQ to traffic that get out from \$TO_R4_if
#pass out quick on \$TO_R4_if proto gre from \$R2 to \$R4 queue VPN4_TO_R4
# PF rules R4 => R2
#pass in quick on \$TO_R4_if proto gre from \$R4 to \$R2 queue VPN4_TO_R4
#pass out quick on \$TO_R2_if proto gre from \$R4 to \$R2 queue VPN4_TO_R2
# ALTQ is disabled since BSDRP 1.81 (too much performance impact)
pass all
EOF
cat > /usr/local/etc/bird.conf <<EOF
# Configure logging
log syslog all;
log "/var/log/bird.log" all;
log stderr all;
# Override router ID
router id 0.0.0.3;
# Sync bird routing table with kernel
protocol kernel kernel4 {
ipv4 {
export all;
};
}
protocol kernel kernel6 {
ipv6 {
export all;
};
}
# Include device route (warning, a device route is a /32)
protocol device {
scan time 10;
}
# Include directly connected networks
protocol direct {
ipv4;
ipv6;
}
protocol rip R4inet4 {
interface "vtnet2","em2" {
version 2;
};
ipv4 {
export all;
};
}
protocol rip ng R4inet6 {
interface "vtnet2","em2" ;
ipv6 {
export all;
};
}
protocol bgp R2inet4 {
local as 100;
# Bird creates IPSEC SAD entry automatically but it need to know the source IP address
# Otherwise it will use the wrong 0.0.0.0 IP as source
source address 10.0.23.3;
neighbor 10.0.23.2 as 100;
password "abigpassword";
ipv4 {
import all;
export all;
};
}
protocol bgp R2inet6 {
local as 100;
# Bird creates IPSEC SAD entry automatically but it need to know the source IP address
# Otherwise it will use the wrong :: IP as source
source address 2001:db8:23::3;
neighbor 2001:db8:23::2 as 100;
password "abigpassword";
ipv6 {
import all;
export all;
};
}
EOF
config save
hostname R3
service netif restart
service pf start
service bird start
Router 4
(you can use script “labconfig vm4” for automatically pushing full configuration):
sysrc hostname=R4
sysrc ifconfig_em3="inet 10.0.45.4/24"
sysrc ifconfig_em3_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:45::4 prefixlen 64"
sysrc ifconfig_em2="10.0.34.4/24 mtu 1528"
sysrc ifconfig_em2_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8:34::4 prefixlen 64"
sysrc cloned_interfaces="lo1"
sysrc ifconfig_lo1="inet 10.0.0.4/32"
sysrc ifconfig_lo1_ipv6="inet6 2001:db8::4 prefixlen 128"
sysrc frr_enable=YES
sysrc frr_vtysh_boot=YES
sysrc mpd_enable=YES
sysrc mpd_flags="-b -s ppp"
sysrc firewall_enable=YES
sysrc firewall_script="/etc/ipfw.rules"
sysrc ipfw_netflow_enable=YES
sysrc ipfw_netflow_ip=10.0.45.5
sysrc ipfw_netflow_port=2055
sysrc ipfw_netflow_version=9
sysrc pimd_enable=YES
ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/rc.conf
cat > /usr/local/etc/frr/frr.conf <<EOF
frr version 7.0
frr defaults traditional
hostname R4
log syslog
!
interface em3
ip router isis BSDRP
ipv6 ospf6 passive
ipv6 router isis BSDRP
!
interface ng0
ip ospf message-digest-key 1 md5 superpass
ip ospf network point-to-point
ipv6 ospf6 passive
!
interface ng1
ipv6 ospf6 network point-to-point
!
!
interface vtnet3
ip router isis BSDRP
ipv6 ospf6 passive
ipv6 router isis BSDRP
!
router-id 0.0.0.4
!
router rip
network lo1
network em2
network vtnet2
version 2
!
router ripng
network lo1
network em2
network vtnet2
!
router ospf
ospf router-id 0.0.0.4
redistribute isis
passive-interface em3
passive-interface vtnet3
network 10.0.4.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
network 10.0.45.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
network 10.4.24.0/24 area 0.0.0.0
area 0.0.0.0 authentication message-digest
!
router ospf6
redistribute isis
interface ng1 area 0.0.0.0
interface vtnet3 area 0.0.0.0
!
router isis BSDRP
is-type level-1-2
net 49.0001.1720.1600.4004.00
redistribute ipv4 ospf level-1
redistribute ipv4 connected level-1
redistribute ipv6 ospf6 level-1
redistribute ipv6 connected level-1
!
line vty
!
bfd
!
EOF
cat > /usr/local/etc/mpd5/if-up.sh <<EOF
#!/bin/sh
set -e
logger "\$0 called with parameters: \$@"
if [ "\$2" == "inet6" ]; then
if ifconfig \$1 \$2 2001:db8:24::4; then
logger "\$0: \$cmd successfull"
return 0
else
logger "\$0: \$cmd failed"
return 1
fi
else
return 0
fi
EOF
chmod +x /usr/local/etc/mpd5/if-up.sh
cat > /usr/local/etc/mpd5/mpd.conf <<EOF
default:
load vpnipv4
load vpnipv6
vpnipv4:
# Create bundle called vpnipv4
create bundle static vpnipv4
# Getting IP from the server
set ipcp ranges 0.0.0.0/0
# Remote LAN subnet: Learned by ISIS
#set iface route 10.0.12.0/24
# Enable Microsoft Point-to-Point encryption (MPPE)
set bundle enable compression
set ccp yes mppc
set mppc yes e40
set mppc yes e128
set bundle enable crypt-reqd
set mppc yes stateless
# Create a static pptp link called lvpnipv4
create link static lvpnipv4 pptp
# Attach this link to vpnipv4
set link action bundle vpnipv4
# Set somes link settings
set link no pap
set link yes chap
set auth authname VpnLogin4
# Reduce the size of the outgoing packet for avoiding fragmentation
set link mtu 1460
set link keep-alive 10 75
# max-redial:
# Server side, need to be "-1"
# Client side, need to be positive (0 for allways)
set link max-redial 0
# Local WAN IP addresse
set pptp self 10.0.0.4
# Remote WAN IP addresse
set pptp peer 10.0.0.2
# Open (initiate) the link to the server
open
vpnipv6:
# Create bundle called vpnipv6
create bundle static vpnipv6
# Getting IP from the server
set ipcp ranges 0.0.0.0/0
# Enable IPv6
set bundle enable ipv6cp
# Remote LAN subnet: Learned by ISIS
#set iface route 2001:db8:12::/64
# Need to statically configure inet6 adress
set iface up-script /usr/local/etc/mpd5/if-up.sh
# Create a static pptp link called lvpnipv6
create link static lvpnipv6 pptp
# Attach this link to vpnipv6
set link action bundle vpnipv6
# Set somes link settings
set link no pap
set link yes chap
set auth authname VpnLogin6
# Reduce the size of the outgoing packet for avoiding fragmentation
set link mtu 1460
set link keep-alive 10 75
# max-redial:
# Server side, need to be "-1"
# Client side, need to be positive (0 for allways)
set link max-redial 0
# Local WAN IP addresse
set pptp self 2001:db8::4
# Remote WAN IP addresse
set pptp peer 2001:db8::2
# Open (initiate) the link to the server
open
EOF
cat > /usr/local/etc/mpd5/mpd.secret <<EOF
VpnLogin4 VpnPassword4
VpnLogin6 VpnPassword6
EOF
echo "# IPFW we need to let it to pass IPv6 Unknown Extension Header for IPv6 PPTP" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
echo "net.inet6.ip6.fw.deny_unknown_exthdrs=0" >> /etc/sysctl.conf
cat > /etc/ipfw.rules <<EOF
#!/bin/sh
fwcmd="/sbin/ipfw"
if ! kldstat -q -m dummynet; then
kldload dummynet
fi
# Flush out the list before we begin.
\${fwcmd} -f flush
# Create hard-limited pipes: One for each direction
\${fwcmd} pipe 60 config bw 20Mbit/s
\${fwcmd} pipe 61 config bw 20Mbit/s
\${fwcmd} pipe 40 config bw 10Mbit/s
\${fwcmd} pipe 41 config bw 10Mbit/s
# Put PPTP Traffic into pipes
\${fwcmd} add pipe 40 all from 10.0.0.4 to 10.0.0.2 out via any
\${fwcmd} add pipe 41 all from 10.0.0.2 to 10.0.0.4 in via any
\${fwcmd} add pipe 60 all from 2001:db8::4 to 2001:db8::2 out via any
\${fwcmd} add pipe 61 all from 2001:db8::2 to 2001:db8::4 in via any
# We don't want to block traffic, only shape some
\${fwcmd} add allow ip from any to any
EOF
config save
hostname R4
service netif restart
service frr start
service mpd5 start
service ipfw start
service sysctl reload
service ipfw_netflow start
service pimd start
Router 1
This router will be used for backuping all other routers configuration files, then it need a root password for enabling SSH access to it. We will use “root” password for this lab.
sysrc hostname=R1 \ gateway_enable=NO \ ipv6_gateway_enable=NO \ ifconfig_em0=up \ cloned_interfaces=lagg0 \ ifconfig_lagg0="laggproto loadbalance laggport em0 SYNCDHCP" \ ifconfig_lagg0_ipv6="inet6 accept_rtadv" \ sshd_enable=yes ifconfig -l | grep -q vtnet && sed -i "" 's/em/vtnet/g' /etc/rc.conf config save hostname R1 service routing restart service netif restart service sshd start
Final testing
IPv4 traffic shaping
From R5, enter jail6 console and launch iperf in IPv4 (default) mode:
[root@R5]~# service jail console jail6 Last login: Sun Jul 2 16:44:12 on ttyu0 BSD Router project (BSDRP) (c) 2009-2017, The BSDRP Development Team All rights reserved. BSDRP is under the Simplified BSD license. Documentation: http://bsdrp.net Discover BSDRP tools with "help" command Keyboard layout can be changed with this command: kbdcontrol -l keymap_file (<TAB> for list available maps) root has logged on ttyu0 from local. [root@jail6]~# iperf3 -s ----------------------------------------------------------- Server listening on 5201 -----------------------------------------------------------
Start an iperf3 client on R1, and check available bandwidth is about 10Mb/s:
[root@R1]~# iperf3 -c 10.0.56.6 Connecting to host 10.0.56.6, port 5201 [ 5] local 10.0.12.1 port 20434 connected to 10.0.56.6 port 5201 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.04 MBytes 8.73 Mbits/sec 0 56.7 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 1.15 MBytes 9.65 Mbits/sec 1 52.3 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.55 Mbits/sec 2 49.6 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.51 Mbits/sec 1 43.8 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 1.13 MBytes 9.46 Mbits/sec 1 38.1 KBytes [ 5] 5.00-6.00 sec 1.15 MBytes 9.66 Mbits/sec 1 35.3 KBytes [ 5] 6.00-7.00 sec 1.15 MBytes 9.61 Mbits/sec 1 1.41 KBytes [ 5] 7.00-8.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.59 Mbits/sec 0 65.1 KBytes [ 5] 8.00-9.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.57 Mbits/sec 1 60.9 KBytes [ 5] 9.00-10.00 sec 1.14 MBytes 9.54 Mbits/sec 1 58.0 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 11.3 MBytes 9.49 Mbits/sec 9 sender [ 5] 0.00-10.04 sec 11.3 MBytes 9.41 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done.
IPv6 traffic shaping
One jail6, display its autoconfigured inet6 address:
[root@jail6]~# ifconfig lagg0 inet6 | grep autoconf
inet6 2001:db8:56:0:ff:ff:fe00:80b prefixlen 64 autoconf
Start an iperf3 ipv6 client on R1, and check available bandwith is about 20Mb/s:
[root@R1]~# iperf3 -c 2001:db8:56:0:cf:8fff:fea9:490b Connecting to host 2001:db8:56:0:cf:8fff:fea9:490b, port 5201 [ 5] local 2001:db8:12:0:5a9c:fcff:fe01:201 port 62845 connected to 2001:db8:56:0:cf:8fff:fea9:490b port 5201 [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr Cwnd [ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.74 MBytes 14.6 Mbits/sec 0 68.2 KBytes [ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 2.23 MBytes 18.7 Mbits/sec 3 65.2 KBytes [ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 2 77.6 KBytes [ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 8 57.1 KBytes [ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 2 38.0 KBytes [ 5] 5.00-6.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 1 61.2 KBytes [ 5] 6.00-7.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.4 Mbits/sec 2 42.1 KBytes [ 5] 7.00-8.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 1 61.2 KBytes [ 5] 8.00-9.00 sec 2.19 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 2 44.8 KBytes [ 5] 9.00-10.00 sec 2.18 MBytes 18.3 Mbits/sec 1 65.3 KBytes - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - [ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr [ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 21.5 MBytes 18.0 Mbits/sec 22 sender [ 5] 0.00-10.03 sec 21.3 MBytes 17.8 Mbits/sec receiver iperf Done. [root@R1]~#
And during iperf, R4 ipfw pipe showing some activity:
root@R4:~ # ipfw pipe show 00040: 10.000 Mbit/s 0 ms burst 0 q131112 50 sl. 0 flows (1 buckets) sched 65576 weight 0 lmax 0 pri 0 droptail sched 65576 type FIFO flags 0x0 0 buckets 0 active 00041: 10.000 Mbit/s 0 ms burst 0 q131113 50 sl. 0 flows (1 buckets) sched 65577 weight 0 lmax 0 pri 0 droptail sched 65577 type FIFO flags 0x0 0 buckets 0 active 00061: 20.000 Mbit/s 0 ms burst 0 q131133 50 sl. 0 flows (1 buckets) sched 65597 weight 0 lmax 0 pri 0 droptail sched 65597 type FIFO flags 0x0 0 buckets 1 active BKT Prot ___Source IP/port____ ____Dest. IP/port____ Tot_pkt/bytes Pkt/Byte Drp 0 ip 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 483 378358 9 6349 0 00060: 20.000 Mbit/s 0 ms burst 0 q131132 50 sl. 0 flows (1 buckets) sched 65596 weight 0 lmax 0 pri 0 droptail sched 65596 type FIFO flags 0x0 0 buckets 1 active 0 ip 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 125 15881 0 0 0
netflow
Check that netflows are collected on jail5 (/tmp/file-date-hour.txt):
[root@jail5]~# ls /tmp/file-* /tmp/file-20170630-0000.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0025.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0005.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0030.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0010.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0035.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0015.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0040.txt /tmp/file-20170630-0020.txt
SNMP
From R1, get 2 SNMP values of R6:
- The basic sysname
- The UCD module version
[root@R1]~# bsnmpget -s 10.0.56.6 sysName.0 sysName.0 = jail6 [root@R1]~# bsnmpwalk -s 10.0.56.6 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.2.0 1.3.6.1.4.1.2021.100.2.0 = $Name: bsnmp-ucd-0-4-3 $
Configurations files network backup
R1 will be use as a configuration files backup repository
Mounting data partition on R1 and configure root password
[root@R1]~# mount /data/ [root@R1]~# passwd Changing local password for root New Password: Retype New Password:
Sending configuration archive file to R1
From all others routers, send the configuration file to the /data partition of R1:
[root@R2]/# config put scp root@10.0.12.1:/data/R2.tar.xz Send saved configuration by SCP to root@10.0.12.1:/data/R2.tar.xz The authenticity of host '10.0.12.1 (10.0.12.1)' can't be established. RSA key fingerprint is 4d:e9:ce:26:d4:2f:92:15:5e:06:97:a8:83:78:0c:e5. Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes Warning: Permanently added '10.0.12.1' (RSA) to the list of known hosts. Password: config.3803.tar.xz 100% 7100 6.9KB/s 00:00
System integrity check
Download the mtree reference file corresponding to your BSDRP release and start a system integrity check. In this lab, we put the reference file in the /tmp folder of R1:
[root@R1]~# system integrity /tmp/BSDRP-1.4-amd64-serial.mtree.xz Here is the modified files comparing to the reference mtree file: dev extra etc extra tmp extra var extra
Extra files and folder are normal regarding your previous tests.